In the business world, entering new markets and expanding market share can be very difficult without strategic partners. Strategic partnerships help companies leverage the resources, experience, and networks of their partners. According to a report by Forbes, more than 50% of international companies rely on strategic partnerships to enter new markets. Additionally, research from McKinsey Institute shows that companies utilizing strategic associations grow, on average, 20% faster than their competitors.
For example, the strategic collaboration between Apple and Foxconn led to large-scale production of Apple products at lower costs and higher efficiency. Similarly, the partnership between Starbucks and Pepsi in distributing Starbucks’ cold beverages increased the market share of both companies. Another example of such partnerships can be seen in the pharmaceutical industry, where large companies like Pfizer and BioNTech successfully collaborated to develop and distribute COVID-19 vaccines.
In this article, we will examine the types of strategic partnerships, criteria for selecting the right partner, the impact of these partnerships on market expansion, and successful examples of them.
Definition of Strategic Partnerships and Their Types
A strategic partnership is a form of business collaboration in which two or more companies work together to achieve common goals. These partnerships can take various forms and play a crucial role in market growth and development. For instance, companies in the technology and pharmaceutical industries use such collaborations to reduce research and development (R&D) costs, improve access to resources, and accelerate the innovation process. Additionally, strategic partnerships enable companies to enter new markets without requiring significant investments, leveraging the expertise and networks of their partners.
Economic data analysis indicates that over the past five years, more than 70% of successful companies in emerging markets have utilized some form of strategic partnership, highlighting the significant role of this strategy in today’s competitive business environment.
Types of Strategic Partnerships
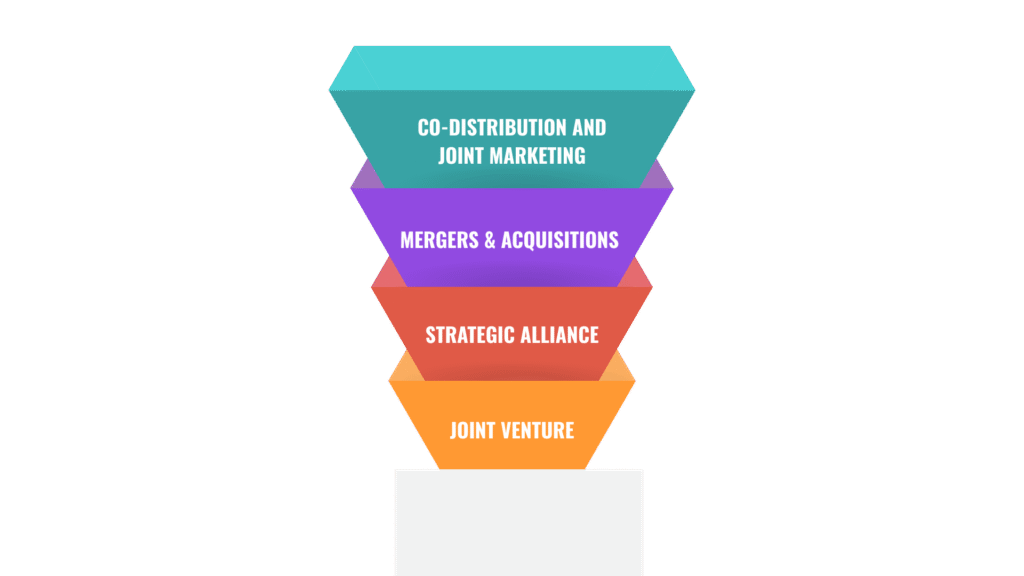
- Joint Venture: Two companies create an independent entity to develop a product or enter a new market, sharing financial resources, technology, and human capital.
- Example: The joint venture between Toyota and Panasonic led to the establishment of a company for producing lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles. Likewise, Honda and GAC formed a joint venture in China to manufacture electric cars, enabling them to enter the clean vehicle market effectively.
- Strategic Alliance: Two companies collaborate for specific objectives without forming a new entity. This collaboration may involve technology sharing, resource pooling, or distribution network integration.
- Example: The partnership between Microsoft and Nokia in developing the Windows Phone operating system was a strategic alliance that allowed Nokia to leverage Microsoft’s software expertise. Similarly, Adidas and Parley for the Oceans collaborated to create sports shoes made from recycled plastics, reducing environmental pollution and promoting sustainability.
- Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A): A company acquires or merges with another firm to gain strategic advantages. This strategy is commonly used to increase market share, reduce operational costs, improve efficiency, and access new technologies.
- Example: The Disney-Fox merger granted Disney greater control over the entertainment industry and expanded its content library for streaming services. Another notable case was Facebook’s (Meta’s) acquisition of WhatsApp, which significantly broadened its user base and service offerings.
- Co-Distribution and Joint Marketing: Companies utilize each other’s distribution and marketing networks to reach new customers, reducing marketing costs, expanding reach, and enhancing brand recognition.
- Example: The Coca-Cola and McDonald’s partnership is a successful model of joint distribution and marketing, with Coca-Cola serving as McDonald’s primary beverage supplier worldwide. Another example is Nike and Apple’s collaboration on Nike+ smart shoes, which strengthened both brands and attracted new customers.
A study published by Harvard Business Review reveals that over 60% of successful companies have engaged in at least one strategic partnership to enter new markets. Furthermore, companies that use strategic collaborations experience an average of 30% revenue growth compared to their competitors.
For instance, the Google-Samsung partnership in artificial intelligence (AI) development introduced innovative features in smart devices, reinforcing both companies’ market positions. Strategic partnerships continue to be a vital tool for business expansion, enabling companies to innovate, optimize costs, and access new opportunities in an increasingly interconnected global economy.
Why Do Startups Need Strategic Partnerships?
Startups often face multiple challenges that can impact their growth and success. Below are some of the key challenges along with explanations and examples:
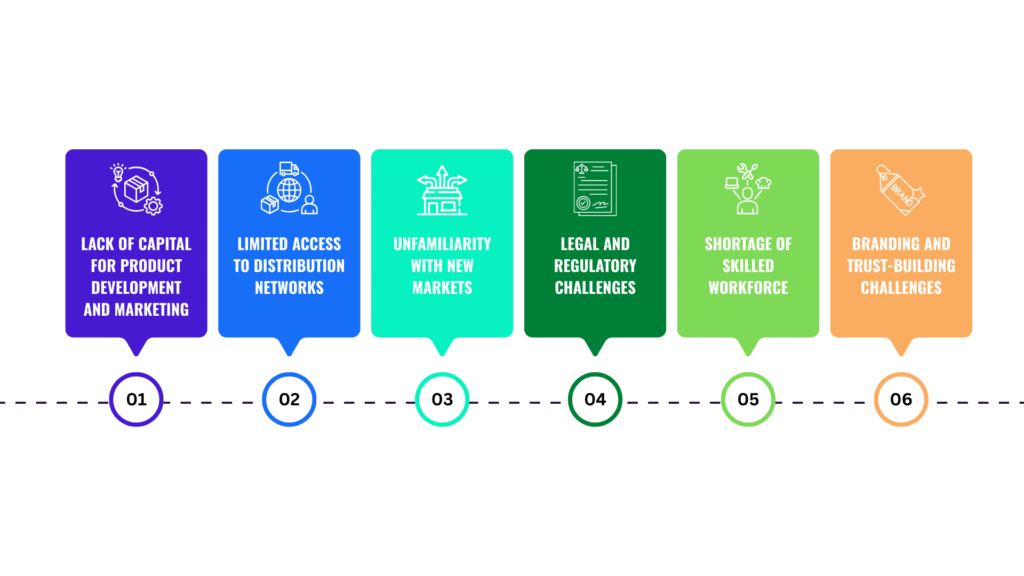
- Lack of Capital for Product Development and Marketing: Many startups struggle with limited financial resources, preventing them from improving their products or running large-scale marketing campaigns.
- Example: In its early stages, Uber needed venture capital investment to cover development and marketing expenses.
- Limited Access to Distribution Networks: Startups typically lack strong distribution channels to reach a larger customer base.
- Example: Spotify, in its early days, partnered with Apple and Facebook to gain wider user access and expand its reach.
- Unfamiliarity with New Markets: Entering new markets comes with unique challenges, such as understanding customer needs and analyzing competitors.
- Example: Alibaba faced significant hurdles when expanding into North America and required local partnerships to navigate the market effectively.
- Legal and Regulatory Challenges: Startups may encounter complex industry regulations and legal requirements.
- Example: Fintech companies like PayPal and Stripe initially faced numerous legal and banking license challenges before establishing themselves.
- Shortage of Skilled Workforce: Many startups require specialized talent to achieve their goals, but hiring skilled professionals can be costly.
- Example: Tesla faced a shortage of battery technology engineers in its early years, slowing down production and innovation.
- Branding and Trust-Building Challenges: New startups often struggle to gain customer trust and compete with well-established brands.
- Example: Airbnb implemented a host verification and review system to enhance trust and security for users, helping it gain credibility in the market.
Strategic partnerships can help startups overcome these challenges by providing financial support, market access, regulatory guidance, talent acquisition, and brand credibility, accelerating their path to success.
How to Choose the Best Strategic Partner for Innovative Businesses
For startups to select the right strategic partner, they must carefully evaluate the following factors:
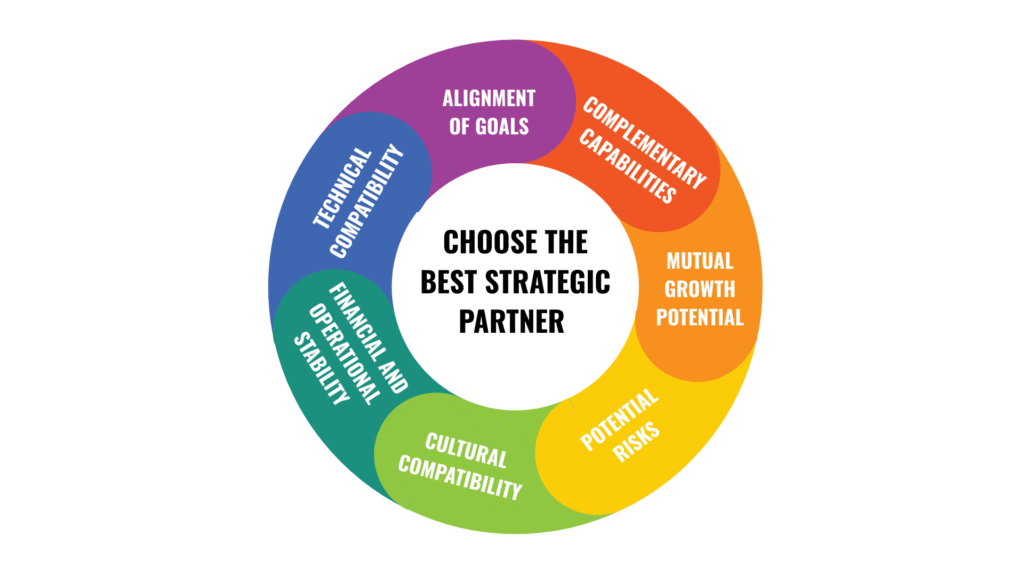
- Alignment of Goals: Ensure that both companies share similar strategic objectives. If their long-term visions differ, the partnership may face difficulties over time. The collaboration between Google and Motorola eventually led to Motorola’s sale due to misalignment in long-term strategies.
- Complementary Capabilities: Each partner should bring resources that compensate for the other’s weaknesses. The Intel-Microsoft (Wintel) partnership enabled Intel to produce powerful processors while Microsoft developed an optimized operating system to support the hardware.
- Mutual Growth Potential: The partnership should contribute to the development of both companies and create shared benefits. The Nike-Apple collaboration on smart shoes enhanced innovation for both companies and expanded their market share.
- Potential Risks: Strategic partnerships can lead to challenges such as over-dependence or loss of brand control. Nokia’s dependence on Microsoft’s Windows Phone platform led to a crisis when the platform failed.
- Cultural Compatibility: Misalignment in corporate culture can cause operational and management issues. The AOL-Time Warner merger failed due to major cultural differences between the two companies.
- Financial and Operational Stability: A financially unstable partner can pose significant risks. The bankruptcy of Solyndra resulted in major losses for its investors and business partners.
- Technical Compatibility and Innovation: If companies use incompatible technologies, collaboration can become challenging. The Sony-Ericsson mobile partnership struggled due to platform incompatibilities and a lack of coordination in new innovations.
Choosing the right strategic partner requires thorough evaluation to ensure long-term success, reduced risks, and maximized innovation potential for both parties.
Impact of Strategic Partnerships on Market Expansion and Revenue Growth
According to a McKinsey & Company report, companies that leverage strategic partnerships to enter new markets experience up to 30% faster growth compared to their competitors. This growth is driven by better access to resources, reduced R&D costs, and increased supply chain efficiency.
A notable example is the Apple-IBM partnership, which focused on developing enterprise software for iOS. This collaboration helped Apple expand its market share in the enterprise sector. By combining Apple’s advanced hardware with IBM’s expertise in data analytics, they created products tailored to large corporations. As a result, Apple strengthened its presence beyond the consumer market and into the enterprise space.
Successful Strategies for Negotiating a Win-Win Partnership
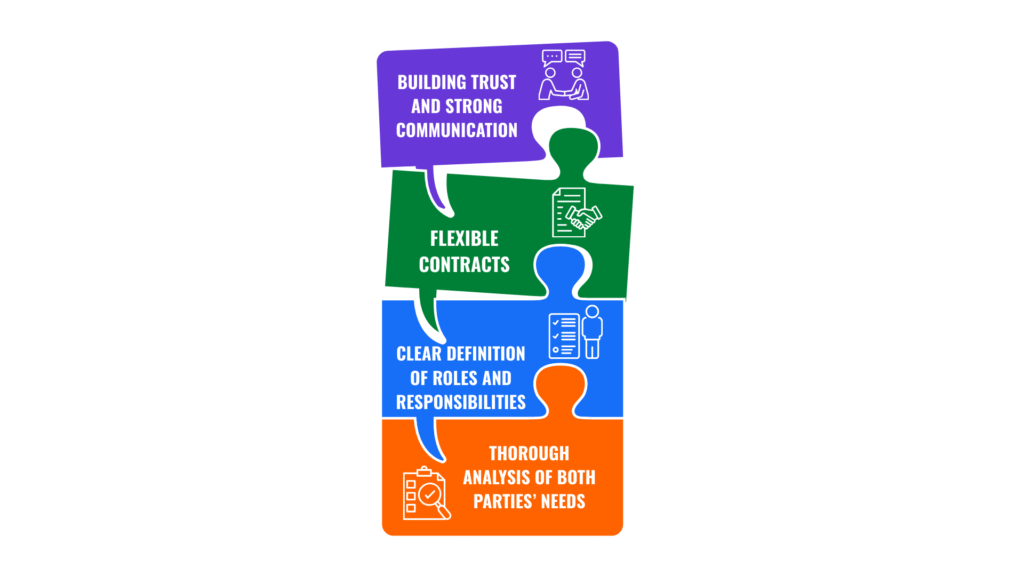
- Thorough Analysis of Both Parties’ Needs: Understanding each company’s strengths and weaknesses is crucial to forming a mutually beneficial partnership. Tesla and Panasonic’s partnership in electric vehicle battery production addressed Tesla’s need for cutting-edge battery technology and Panasonic’s need for a broader market. This resulted in cost-efficient and high-performance batteries.
- Clear Definition of Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly outlining each party’s responsibilities minimizes conflicts and misunderstandings. The Google-Samsung partnership in Pixel phone development was based on Google handling software design while Samsung supplied hardware components, leading to an optimized process.
- Flexible Contracts: Allowing for adaptability to market conditions ensures long-term success. Microsoft and Intel’s collaboration on processors and operating systems involved flexible agreements, enabling them to adjust their partnership based on technological advancements and market demands.
- Building Trust and Strong Communication: Regular meetings and open communication help resolve conflicts and enhance coordination. During Pfizer and BioNTech’s partnership in COVID-19 vaccine development, continuous information exchange and frequent meetings enabled them to produce an effective vaccine in record time.
By implementing these strategies, companies can maximize the success and longevity of their strategic partnerships, leading to market expansion, higher revenue, and sustainable competitive advantage.
Challenges of Strategic Partnerships and Management Solutions
- Misalignment of Strategic Goals: Differences in vision can lead to ineffective collaboration. The failed Nokia-Microsoft partnership was due to differing focuses on software and hardware. Establishing clear performance metrics and holding regular joint meetings can help align strategies.
- Unequal Profit Distribution: Disproportionate benefit-sharing can cause dissatisfaction. Apple’s suppliers often feel that Apple retains most of the profits. Transparency in revenue models and profit-sharing based on value contribution can diminish conflicts.
- Cultural Differences: Different management styles can hinder productivity. The Daimler-Chrysler merger failed due to organizational culture clashes. Workshops and employee exchange programs can enhance alignment.
- Legal and Financial Risks: Legal and financial complications can disrupt partnerships. The Sony-BMG merger faced legal challenges. Well-structured contracts and legal advisors can help prevent disputes.
- Operational and Technological Barriers: Incompatible technologies can hinder integration. The Airbus-Boeing partnership faced data management issues due to system mismatches. Using shared platforms and technology harmonization can improve efficiency.
The Role of Networking and Trade Events in Strategic Partnerships
Industry trade events and technology conferences provide ideal platforms for businesses to establish new connections and partnerships. These events allow companies to showcase their products and services, network with potential partners, and explore strategic collaboration opportunities. For example, CES (Consumer Electronics Show) attracts over 4,500 technology companies and 175,000 attendees from 150 countries annually, making it an ideal venue for startups to connect with investors, business partners, and new customers. Other major networking events include:
- Hannover Messe (for industrial technology)
- Mobile World Congress (MWC) (for telecommunications and mobile innovations)
These events serve as powerful catalysts for forming strategic alliances and fostering innovation-driven growth.
Conclusion
Strategic partnerships are one of the most effective ways to expand market reach and enhance business competitiveness. These collaborations enable companies to leverage the expertise, resources, and distribution networks of their partners without requiring heavy investments. Economic data and various studies indicate that companies relying on strategic partnerships experience higher growth and efficiency compared to their competitors. Successful examples in the technology, pharmaceutical, and retail industries confirm that well-planned collaborations can facilitate effective entry into new markets.
Selecting the right partner is crucial for the success of such collaborations. Factors such as goal alignment, complementary capabilities, mutual growth potential, and cultural compatibility should be carefully evaluated before forming a strategic partnership. Failed collaborations highlight that misaligned strategies, financial disputes, and cultural differences are key reasons for unsuccessful partnerships. Therefore, having a clear strategy, establishing well-defined contracts, and continuously managing the business relationship can reduce potential risks.
Challenges such as unequal profit distribution, legal risks, technological differences, and operational issues are common obstacles in strategic partnerships. However, companies that adopt flexible approaches, transparent revenue models, and shared platforms have successfully managed these challenges. Effective communication and regular meetings between partners also play a crucial role in ensuring the success of strategic collaborations.
Finally, networking and participation in trade events are essential for identifying partnership opportunities. Industry exhibitions, technology conferences, and business summits provide companies with a valuable platform to connect with potential partners. Given the increasing competition in global markets, leveraging strategic partnerships can pave the way for the success of innovative businesses.





